ถ้าตามที่ได้คุยกันคือบวกจุดบานปลายแล้วไม่เกิน4000 ก็ลงมือไปเลยครับ
กลางกับแหลมที่ผมพอใจคือความสมดุลของปริมานเสียงครับ ถ้าเปลี่ยนอะหลั่ยแล้วมันช่วยเรื่องเนื้อที่ดี รายละเอียดดีขึ่นไปอีกก็ไม่มีปัญหาครับ
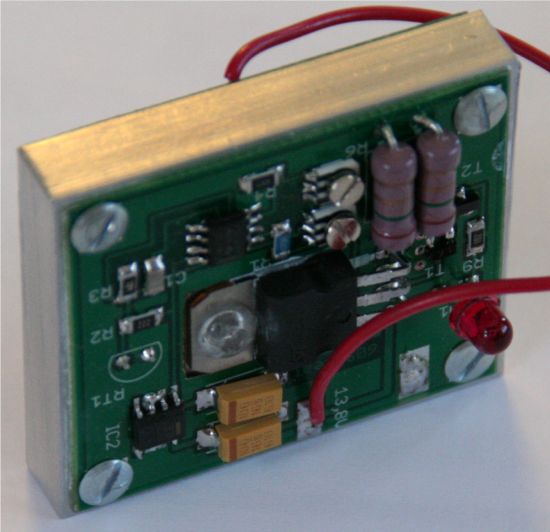
Cตัวที่ว่ามีคราบดำๆนี่ตรงจุดแถวไหนครับ
กลางกับแหลมที่ผมพอใจคือความสมดุลของปริมานเสียงครับ ถ้าเปลี่ยนอะหลั่ยแล้วมันช่วยเรื่องเนื้อที่ดี รายละเอียดดีขึ่นไปอีกก็ไม่มีปัญหาครับ
Cตัวที่ว่ามีคราบดำๆนี่ตรงจุดแถวไหนครับ


















Comment