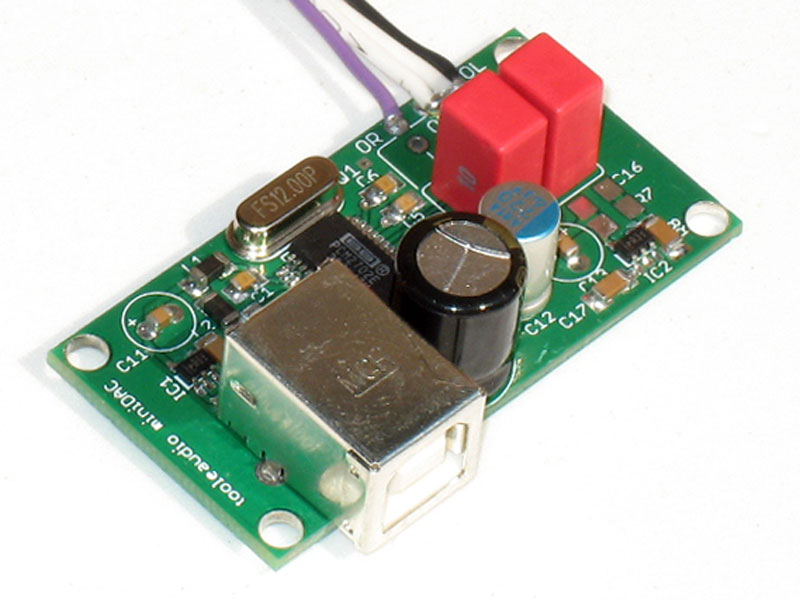
^^ อ้อ... ขอบคุณครับ NPE เอ ทำไมผมเห็นมัน 550:- ล่ะ สงสัยลืมดูน้ำหนัก  อันนี้มัน 150g.
อันนี้มัน 150g.
-----------------
ตามมาอยากรู้แหล่งขายในเมืองไทย ที่คุณkeang ถามด้วยคน
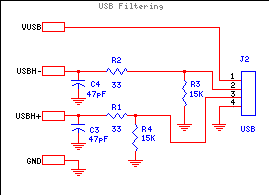
พวก IC พวกนี้ส่วนใหญ่ผมก็สั่งเอาจากเมืองนอกหาง่ายดี แต่รวมๆแล้วแพงงหน่อย
ส่วนมากก็สั่งเอาจาก Farnell(element14) หรือ RS น่ะครับ ค่าส่งถูก - ไม่มีค่าส่ง
 อันนี้มัน 150g.
อันนี้มัน 150g. -----------------
ตามมาอยากรู้แหล่งขายในเมืองไทย ที่คุณkeang ถามด้วยคน
พวก IC พวกนี้ส่วนใหญ่ผมก็สั่งเอาจากเมืองนอกหาง่ายดี แต่รวมๆแล้วแพงงหน่อย

ส่วนมากก็สั่งเอาจาก Farnell(element14) หรือ RS น่ะครับ ค่าส่งถูก - ไม่มีค่าส่ง





















Comment